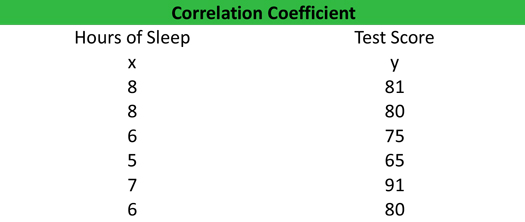
Coefficient Of Correlation Example - Financial ratios are essential in evaluating businesses and their performance in the market. One of these ratios that you should know is the correlation coefficient. The correlation coefficient measures the relationship between two variables. A coefficient of correlation ranges from -1 to +1, which means that the closer it is to -1, the stronger the inverse relationship, while the closer it is to +1, the stronger the correlation. In this article, you will learn more about the correlation coefficient, its formula, calculation, and analysis, as well as how to interpret its results.
Pearson Correlation Coefficient Formula
Example | Calculation | Analysis
The Pearson correlation coefficient formula is the most common method used in measuring the linear relationship between two variables. You can use it to determine if there is a positive correlation, negative correlation, or no correlation at all. The formula is:
Where:
- rxy - Pearson correlation coefficient between x and y
- n - number of observations
- ∑ - summation
- xi - value of x
- xbar - mean of x
- yi - value of y
- ybar - mean of y
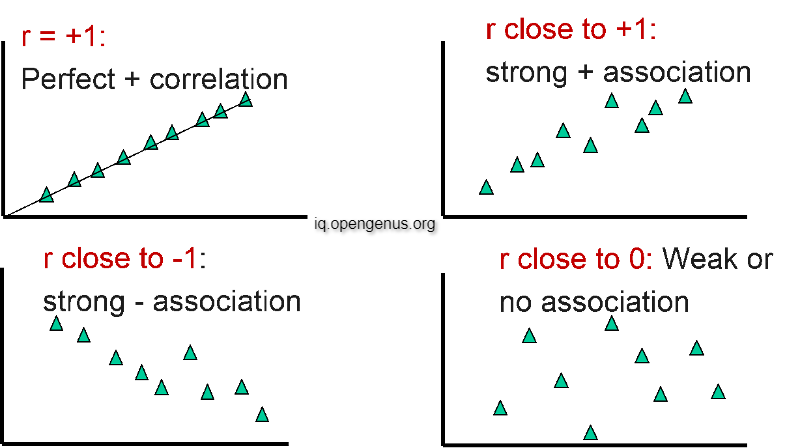
Correlation (r)
Data Analyze
The correlation coefficient, represented by r, is a measure of the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. The value of r can range from -1 to +1, where -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, 0 indicates no correlation, and +1 indicates a perfect positive correlation. Here's how you can interpret the value of r:
- -1 ≤ r ≤ -0.7 Strong Negative Correlation
- -0.7 ≤ r ≤ -0.3 Moderate Negative Correlation
- -0.3 ≤ r ≤ -0.1 Weak Negative Correlation
- -0.1 ≤ r ≤ 0.1 No Correlation
- 0.1 ≤ r ≤ 0.3 Weak Positive Correlation
- 0.3 ≤ r ≤ 0.7 Moderate Positive Correlation
- 0.7 ≤ r ≤ 1 Strong Positive Correlation
When analyzing correlation, it is important to also consider outliers or extreme values, as they can significantly affect the correlation coefficient.
Regression vs Correlation
Regression and correlation are two statistical concepts that are often used interchangeably but have different meanings. Regression is used to examine the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. Correlation, on the other hand, measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables, regardless if one is dependent and the other is independent.
Both regression and correlation can be used to make predictions, but regression is more commonly used for prediction purposes since it involves an independent variable. Correlation, on the other hand, is more commonly used to examine the relationship between two variables and determine the strength of their association.
Pearson Correlation Coefficient: Calculation + Examples
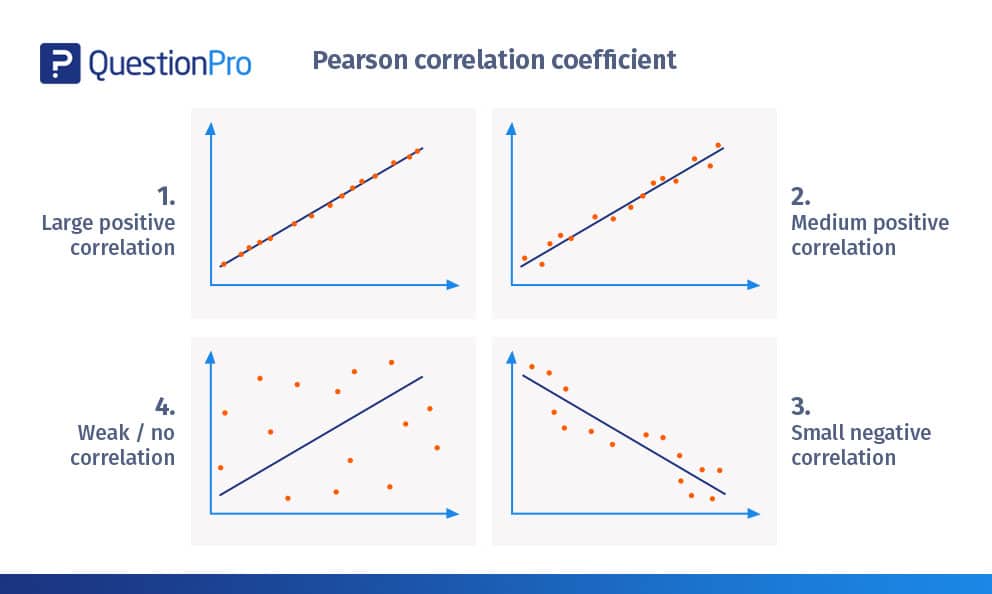
The Pearson correlation coefficient is widely used in many fields, including finance, marketing, and psychology. Here are some examples of how it can be used:
- In finance, the Pearson correlation coefficient is used to measure the degree to which the prices of two assets move in relation to each other. For example, if an investor holds two stocks, they can use the Pearson correlation coefficient to determine if the prices of the two stocks move in the same direction or not.
- In marketing, the Pearson correlation coefficient can be used to measure the association between two variables, such as advertising expenses and sales. This can help marketers determine how much they should spend on advertising in order to achieve a certain level of sales.
- In psychology, the Pearson correlation coefficient is used to measure the degree to which two psychological tests are related. For example, psychologists can use it to determine if a person's performance on one test can predict their performance on another test.
When interpreting the results of the Pearson correlation coefficient, it is important to consider not just the value of r but also the significance of the p-value. A p-value of less than 0.05 indicates that the coefficient is significant, while a p-value greater than 0.05 indicates that the coefficient is not significant.
Correlation Coefficient & Its Types
Formula & Derivation | Math
There are three types of correlation coefficients: Pearson's, Spearman's, and Kendall's. Pearson's correlation coefficient measures the strength of the linear relationship between two variables, while Spearman's and Kendall's measure the strength of the monotonic relationship between two variables. A monotonic relationship is a relationship that does not necessarily have a linear pattern but still follows a consistent pattern.
When selecting the type of correlation coefficient to use, it is important to consider the type of data you have and the nature of the relationship between the two variables. Pearson's correlation coefficient is suitable for continuous data while Spearman's and Kendall's are suitable for ordinal data.
Tips, Ideas, and How To:
Here are some tips, ideas, and how-to's when using the correlation coefficient in your analysis:
- Always test for statistical significance to ensure the results are valid.
- Always consider the context of the data before interpreting the results of the correlation coefficient.
- Be careful not to assume causation even if there is a strong correlation between two variables.
- When selecting the type of correlation coefficient to use, consider the type of data you have and the nature of the relationship between the two variables.
- Consider using scatter plots to visualize the relationship between two variables.
- If you have a large sample size, consider using the sample correlation coefficient instead of the population correlation coefficient formula for better accuracy.
- Always be clear and explicit in reporting the results of the correlation coefficient, including the value of r and the p-value, as well as their interpretation.
By understanding the correlation coefficient, how to calculate it, and how to interpret its results, you can gain valuable insights into the relationship between two variables and make informed decisions based on your analysis.
Find more articles about Coefficient Of Correlation Example


