Example Of A Controlled Experiment - A controlled experiment is a scientific study that involves manipulating one variable while keeping all other variables constant. This allows scientists to determine if the variable being manipulated causes a change in the outcome. In this post, we will look at different examples of controlled experiments, explain what they are, and provide tips for conducting your own controlled experiments.
Biology: Controlled Experiments
Title: Biology: Controlled Experiments - YouTube
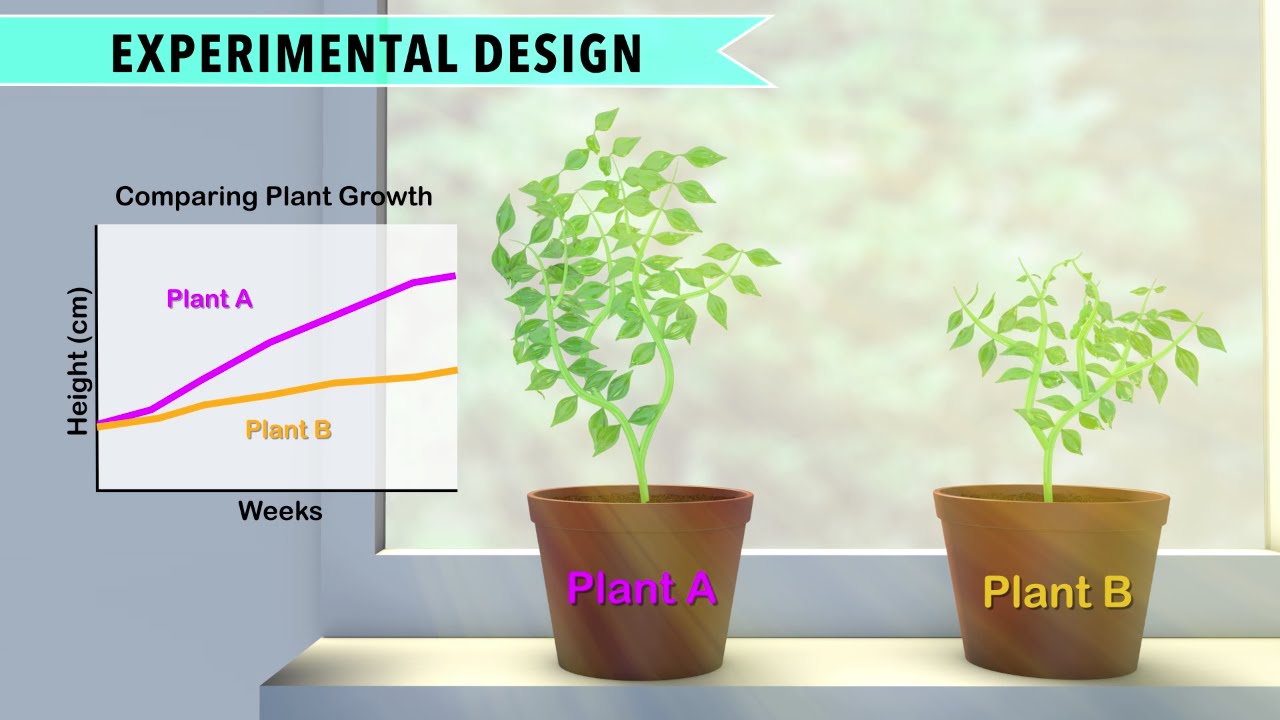 In biology, controlled experiments are used to test hypotheses about how different factors affect living organisms. For example, if a scientist wanted to know if a new fertilizer increased crop yields, they might conduct a controlled experiment by dividing a field into two groups. One group would receive the new fertilizer, and the other group would receive the old fertilizer. All other variables, such as the amount of water and sunshine the plants received, would be kept constant. By comparing the crop yields of the two groups, the scientist could determine if the new fertilizer was effective.
In biology, controlled experiments are used to test hypotheses about how different factors affect living organisms. For example, if a scientist wanted to know if a new fertilizer increased crop yields, they might conduct a controlled experiment by dividing a field into two groups. One group would receive the new fertilizer, and the other group would receive the old fertilizer. All other variables, such as the amount of water and sunshine the plants received, would be kept constant. By comparing the crop yields of the two groups, the scientist could determine if the new fertilizer was effective.
Science uses controlled experiments to test models
Title: Science uses controlled experiments to test models. | Science or not?
 Scientists use controlled experiments to test their models and hypotheses. This allows them to see if their models accurately predict real-world phenomena. For example, if a scientist wanted to test whether their model predicted how fast a ball would fall, they might conduct a controlled experiment by dropping identical balls from the same height and measuring how fast they fall. By comparing the predicted rate of fall from the model to the actual rate of fall, the scientist could determine if their model was accurate.
Scientists use controlled experiments to test their models and hypotheses. This allows them to see if their models accurately predict real-world phenomena. For example, if a scientist wanted to test whether their model predicted how fast a ball would fall, they might conduct a controlled experiment by dropping identical balls from the same height and measuring how fast they fall. By comparing the predicted rate of fall from the model to the actual rate of fall, the scientist could determine if their model was accurate.
Difference between Controlled Group and Controlled Variable in an Experiment
Title: Difference between Controlled Group and Controlled Variable in an Experiment
 It's important to understand the difference between a controlled group and a controlled variable in a controlled experiment. A controlled group is a group that is used as a comparison in an experiment. For example, if a scientist wanted to test whether a new drug cured a disease, they might divide their participants into two groups. One group would receive the new drug, and the other group would receive a placebo. The placebo group acts as the controlled group. A controlled variable, on the other hand, is a variable that is kept constant throughout the experiment. This allows the scientist to isolate the effects of the manipulated variable. For example, if a scientist wanted to test the effect of temperature on plant growth, they might keep all other variables, such as light and soil nutrients, constant. This allows them to see if temperature has an effect on plant growth.
It's important to understand the difference between a controlled group and a controlled variable in a controlled experiment. A controlled group is a group that is used as a comparison in an experiment. For example, if a scientist wanted to test whether a new drug cured a disease, they might divide their participants into two groups. One group would receive the new drug, and the other group would receive a placebo. The placebo group acts as the controlled group. A controlled variable, on the other hand, is a variable that is kept constant throughout the experiment. This allows the scientist to isolate the effects of the manipulated variable. For example, if a scientist wanted to test the effect of temperature on plant growth, they might keep all other variables, such as light and soil nutrients, constant. This allows them to see if temperature has an effect on plant growth.
Experimental Design - Controlled Experiment
Title: Experimental Design - Controlled Experiment - YouTube
 Before conducting a controlled experiment, it's important to have a well-designed experimental plan. This includes clearly defining the variables you will be manipulating and measuring, identifying a control group, and deciding how participants or subjects will be allocated to different groups. It's also important to ensure that all other variables are kept constant throughout the experiment. By carefully designing your experiment, you can ensure that your results are accurate and meaningful.
Before conducting a controlled experiment, it's important to have a well-designed experimental plan. This includes clearly defining the variables you will be manipulating and measuring, identifying a control group, and deciding how participants or subjects will be allocated to different groups. It's also important to ensure that all other variables are kept constant throughout the experiment. By carefully designing your experiment, you can ensure that your results are accurate and meaningful.
Experiment clipart dependent variable
Title: Experiment clipart dependent variable
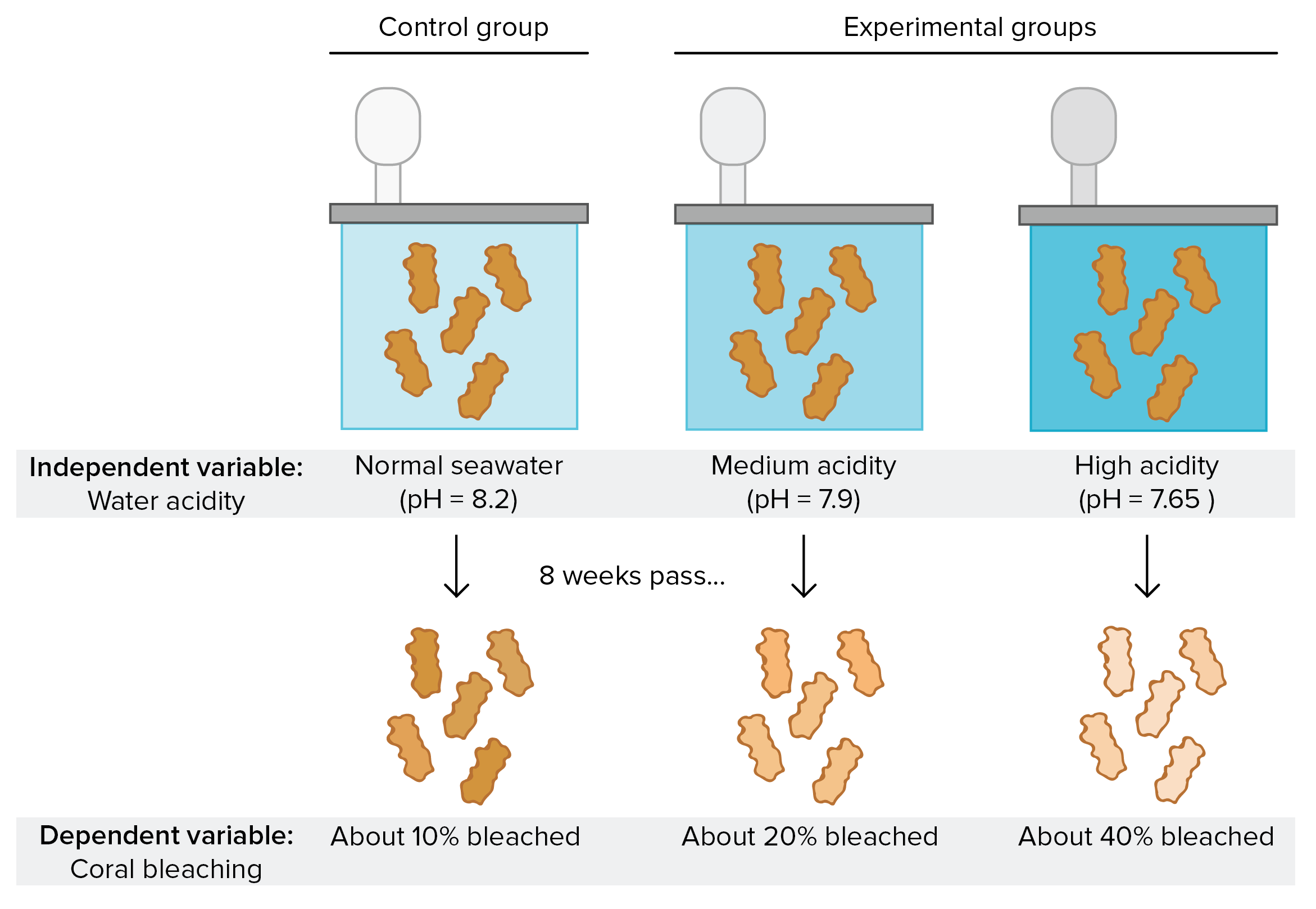 In a controlled experiment, it's important to identify the dependent variable. The dependent variable is the variable that is being measured or observed. For example, if a scientist is conducting an experiment to see if caffeine affects reaction time, reaction time would be the dependent variable. By measuring the dependent variable, the scientist can see if there is a difference between the group receiving caffeine and the group not receiving caffeine. This allows them to determine if caffeine affects reaction time.
In a controlled experiment, it's important to identify the dependent variable. The dependent variable is the variable that is being measured or observed. For example, if a scientist is conducting an experiment to see if caffeine affects reaction time, reaction time would be the dependent variable. By measuring the dependent variable, the scientist can see if there is a difference between the group receiving caffeine and the group not receiving caffeine. This allows them to determine if caffeine affects reaction time.
Tips for Conducting Controlled Experiments
Here are some tips for conducting your own controlled experiments:
- Clearly define the variables you will be manipulating and measuring.
- Identify a control group that can be used as a comparison.
- Ensure that all other variables are kept constant throughout the experiment.
- Randomly assign subjects or participants to different groups to help control for differences between individuals.
- Collect data carefully and accurately.
- Use appropriate statistical tests to analyze your data.
Ideas for Controlled Experiments
Here are some ideas for controlled experiments:
- Does drinking caffeine increase reaction time?
- Does listening to music affect test scores?
- Does exercise increase weight loss?
- Does temperature affect seed germination?
- Does sugar affect blood pressure?
How to Conduct a Controlled Experiment
Here are the steps to conduct a controlled experiment:
- Identify your research question.
- Define your dependent variable.
- Identify your independent variable(s).
- Identify any potential confounding variables.
- Design your experiment, including your control group and how you will allocate subjects to different groups.
- Conduct your experiment, ensuring that all other variables are kept constant.
- Collect data carefully and accurately.
- Use appropriate statistical tests to analyze your data.
- Draw conclusions and communicate your findings.
By following these steps and tips, you can conduct your own controlled experiments and contribute to the scientific knowledge base.
Read more articles about Example Of A Controlled Experiment


