First Law of Thermodynamics With Example - Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that deals with the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another. This means that the total energy of a system remains constant. In this article, we will discuss the first law of thermodynamics and its applications.
First Law of Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics is also known as the law of conservation of energy. It states that the total energy of a system and its surroundings remains constant, irrespective of the changes that may take place in the system or its surroundings. This law is based on the observation that energy always transforms from one form to another and that it is never completely lost.
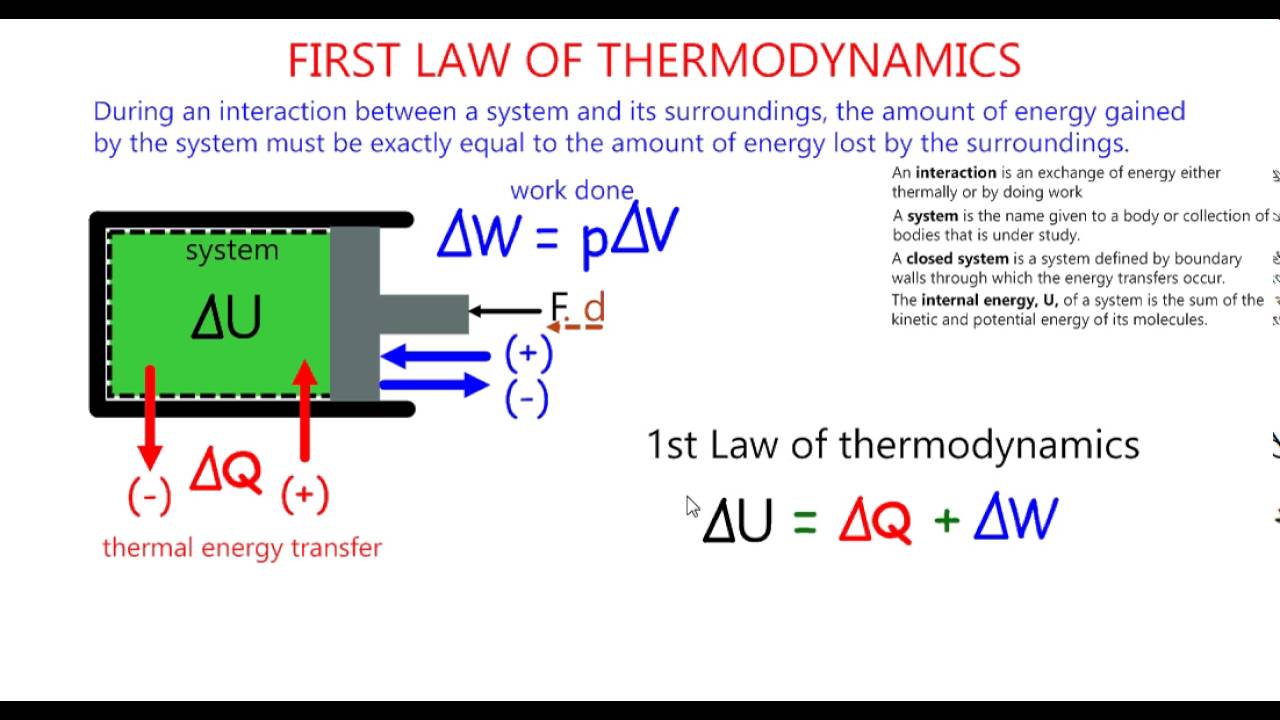
Applications of First Law of Thermodynamics
The first law of thermodynamics finds its application in various fields, including physics, chemistry, mechanical engineering, and electrical engineering. Below are some examples of how the first law of thermodynamics is applied in different fields.
Physics
The first law of thermodynamics is used in the study of heat engines such as steam engines, refrigerators, and air conditioning systems. It is also used in the study of thermodynamic systems and their properties.
Chemistry
The first law of thermodynamics is used in the study of chemical reactions and their energy changes. It is also used in the study of phase transitions, such as solid-to-liquid and liquid-to-gas transitions.
Mechanical Engineering
The first law of thermodynamics is used in the design and analysis of engines, turbines, and other machines that use thermal energy. It is also used in the study of thermodynamics and heat transfer.
Electrical Engineering
The first law of thermodynamics is used in the study of electrical power generation and distribution. It is also used in the design and analysis of electrical machines such as motors and generators.
Energy and Work
Energy is the ability to perform work. Work is a measure of the force required to move an object over a certain distance. The first law of thermodynamics relates energy and work through the following equation:
ΔE = Q - W
Where ΔE is the change in internal energy of a system, Q is the heat transferred to the system, and W is the work done by the system.
Heat and Temperature
Heat is defined as the transfer of thermal energy from a hot object to a cooler object. Heat flows from a higher temperature object to a lower temperature object. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
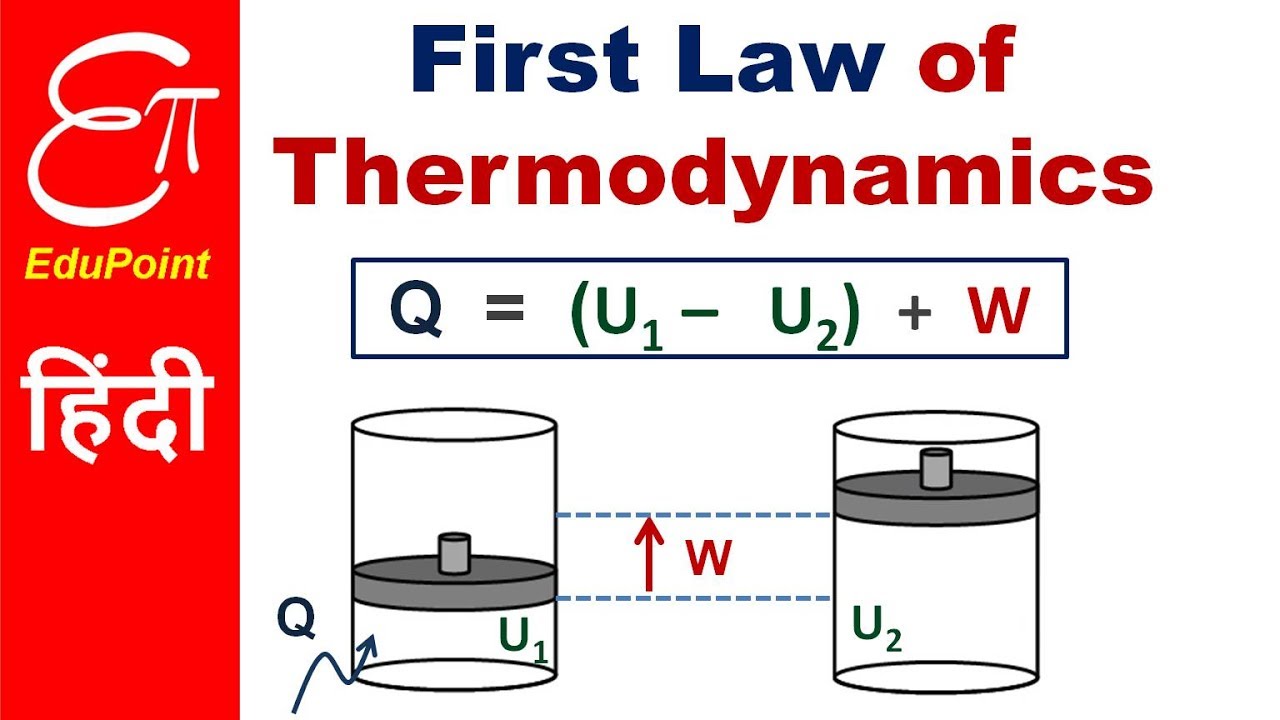
Tips and Ideas
Below are some tips and ideas related to the first law of thermodynamics:
Energy Conservation
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another. This means that we should conserve energy whenever possible, by using energy-efficient appliances and reducing our consumption of fossil fuels.
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower are sustainable and do not produce greenhouse gases. Using renewable energy sources can help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change.
Insulation
Insulating our homes and buildings can help reduce energy consumption by keeping the interior temperature constant. This can be achieved by using insulation materials such as fiberglass, cellulose, or foam.
Recycling
Recycling conserves energy by reducing the amount of energy needed to extract and process new raw materials. By recycling, we can also reduce our carbon footprint and help protect the environment.

How To
Below are some ways to apply the first law of thermodynamics:
Energy Audit
An energy audit is a comprehensive survey of a building to determine its energy consumption and identify ways to reduce it. It involves analyzing the building's heating and cooling systems, lighting, and appliances, as well as its insulation and ventilation.
Energy-Efficient Appliances
Purchasing energy-efficient appliances can help reduce energy consumption and save money on utility bills. Energy Star certified appliances use less energy than standard appliances and can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Renewable Energy Systems
Installing renewable energy systems such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and lower energy bills. These systems can also qualify for tax incentives and other government subsidies.
Green Building Design
Green building design involves using sustainable materials, energy-efficient systems, and renewable energy sources to create buildings that are environmentally friendly and energy-efficient. This can be achieved through the use of green roofs, rainwater harvesting, and other innovative technologies.

In conclusion, the first law of thermodynamics is a fundamental principle that governs the behavior of energy in various systems. It has important applications in physics, chemistry, mechanical engineering, and electrical engineering. By understanding the first law of thermodynamics, we can make informed decisions to conserve energy, reduce our carbon footprint, and protect the planet for future generations.
View more articles about First Law Of Thermodynamics With Example


