What Is An Example Of Prokaryotic Cell - Prokaryotic cells are a type of cell that lacks a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are unicellular microorganisms and are found in various environments such as soil, water, and even in the human body. Prokaryotic cells can be bacterial or archaeal, and they have several unique characteristics that distinguish them from eukaryotic cells. In this article, we will explore some examples of prokaryotic cells, their structure, and their functions.
Examples of Prokaryotic Cells
Bacteria
Bacteria are the most well-known type of prokaryotic cells. They are found in a variety of ecosystems and have diverse metabolic capabilities. Bacteria can be classified based on their shape (cocci, bacilli, spirilla), their ability to form colonies, and their need for oxygen. Some examples of bacteria are:

- E. coli – a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium
- Staphylococcus aureus – a Gram-positive, round-shaped bacterium
- Cyanobacteria – a group of photosynthetic bacteria that can produce oxygen
Archaea
Archaea are another type of prokaryotic cell that can be found in extreme environments such as hot springs, deep sea vents, and salt lakes. They have unique membrane lipids and can survive in harsh conditions. Examples of archaeal cells are:
- Methanogens – a group of archaea that produce methane as a metabolic by-product
- Halophiles – archaea that can tolerate high salt concentration
- Thermophiles – archaea that can survive in extremely hot environments
Structure of Prokaryotic Cells
Cell Wall
Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall that provides structural support and protection. Bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan, which is a polymer of sugars and amino acids. Archaeal cell walls are made of different substances such as pseudopeptidoglycan or S-layer proteins.
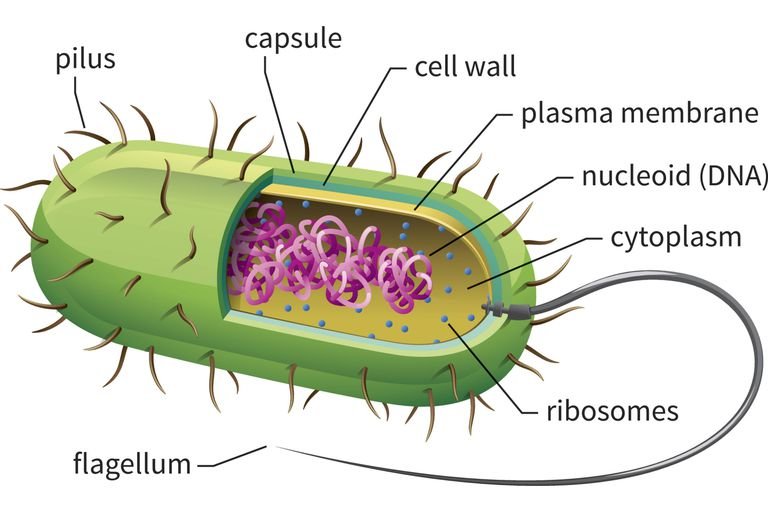
Capsule
Some prokaryotic cells have a capsule, which is a layer of polysaccharides that provides protection against the host's immune system. The capsule also helps the cell attach to surfaces and can aid in bacterial motility.
Pili
Prokaryotic cells may also produce pili, which are hair-like structures that aid in attachment to surfaces and other cells. Pili can also be involved in conjugation, which is the transfer of genetic material between cells.
Functions of Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells have several important functions in various ecosystems, including:
Decomposition
Prokaryotic cells play a crucial role in breaking down dead organic material in the environment. Bacteria and archaea secrete enzymes that can break down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds that can be used by other organisms.
Nutrient Cycling
Prokaryotic cells are also involved in nutrient cycling, which is the process of recycling nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in ecosystems. Bacteria can fix nitrogen from the atmosphere and make it available to other organisms, while methanogens can produce methane as a by-product of metabolism.
Pathogenesis
Some prokaryotic cells can cause disease in humans and animals. Examples of pathogenic bacteria include Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus pneumoniae. These bacteria can cause infections such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and meningitis.
Tips, Ideas, and How To:
If you are interested in learning more about prokaryotic cells, here are some tips, ideas, and how-to's:
Visit a Microbiology Museum
There are several museums around the world that are dedicated to microbiology and showcase the diversity of microorganisms. These museums can be a great resource for learning about prokaryotic cells and their functions.
Do a Microbial Ecology Experiment
You can set up an experiment to investigate the functions of prokaryotic cells in your own backyard or local environment. You can collect soil or water samples and analyze the microbial communities present using techniques such as DNA sequencing or microscopy.
Read Scientific Articles and Journals
Scientific articles and journals are a great resource for learning about the latest research on prokaryotic cells. You can find articles in open access journals such as PLOS ONE or by browsing databases such as PubMed.
In conclusion, prokaryotic cells are a fascinating group of microorganisms that have important functions in various ecosystems. By understanding their structure and functions, we can appreciate the diversity of life on Earth and the role that microorganisms play in shaping our planet.View more articles about What Is An Example Of Prokaryotic Cell


